02 Sep 2021 - Tags: analysis-qual-prep
On to day Yesterday Tuesday1 was all about measures
and integrable functions. Today, then, let’s talk about spaces of integrable
functions. It’s time for
Thankfully, this should be a comparatively short post, since
The lower values of
Conversely, large values of
As an example, think of
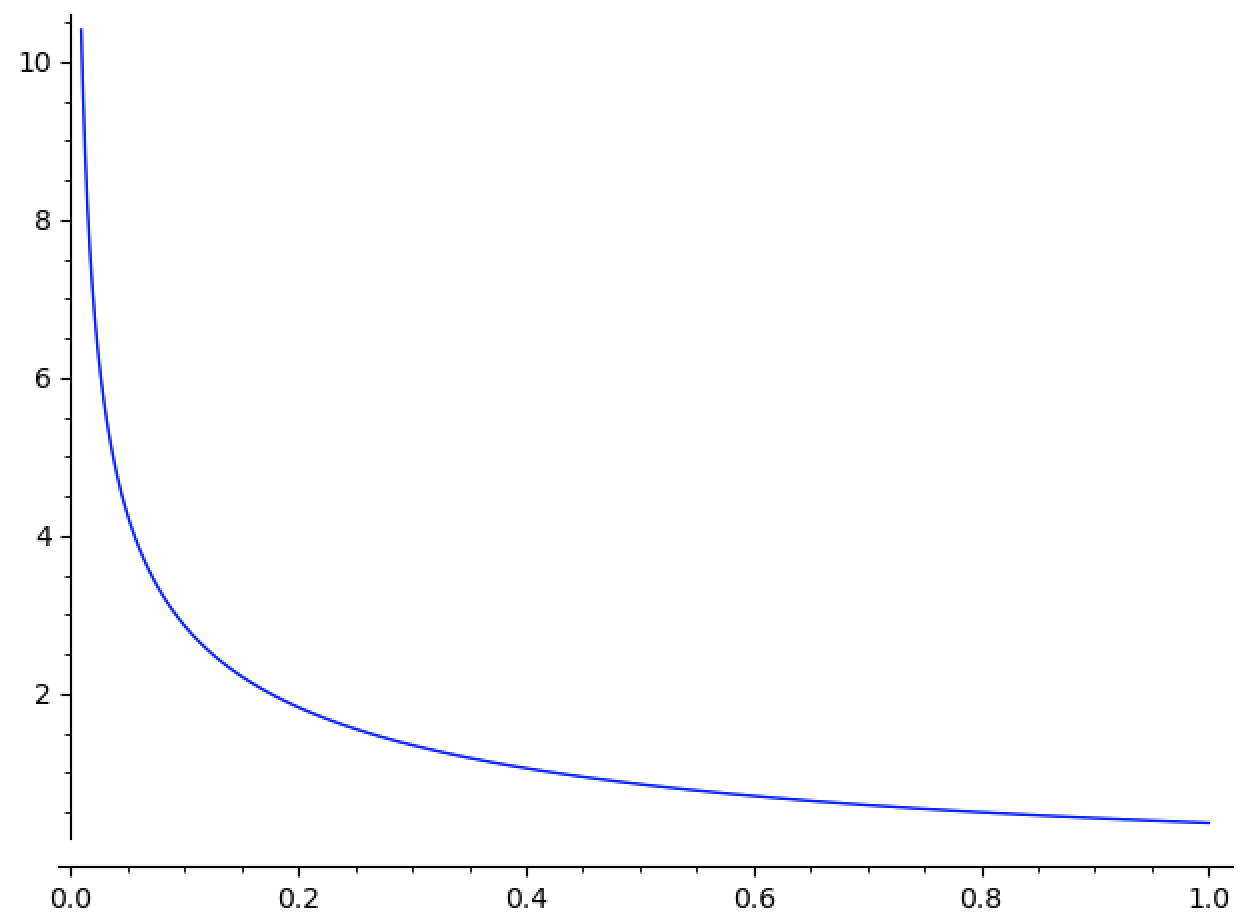
This has a singularity at
Conversely, consider the constant
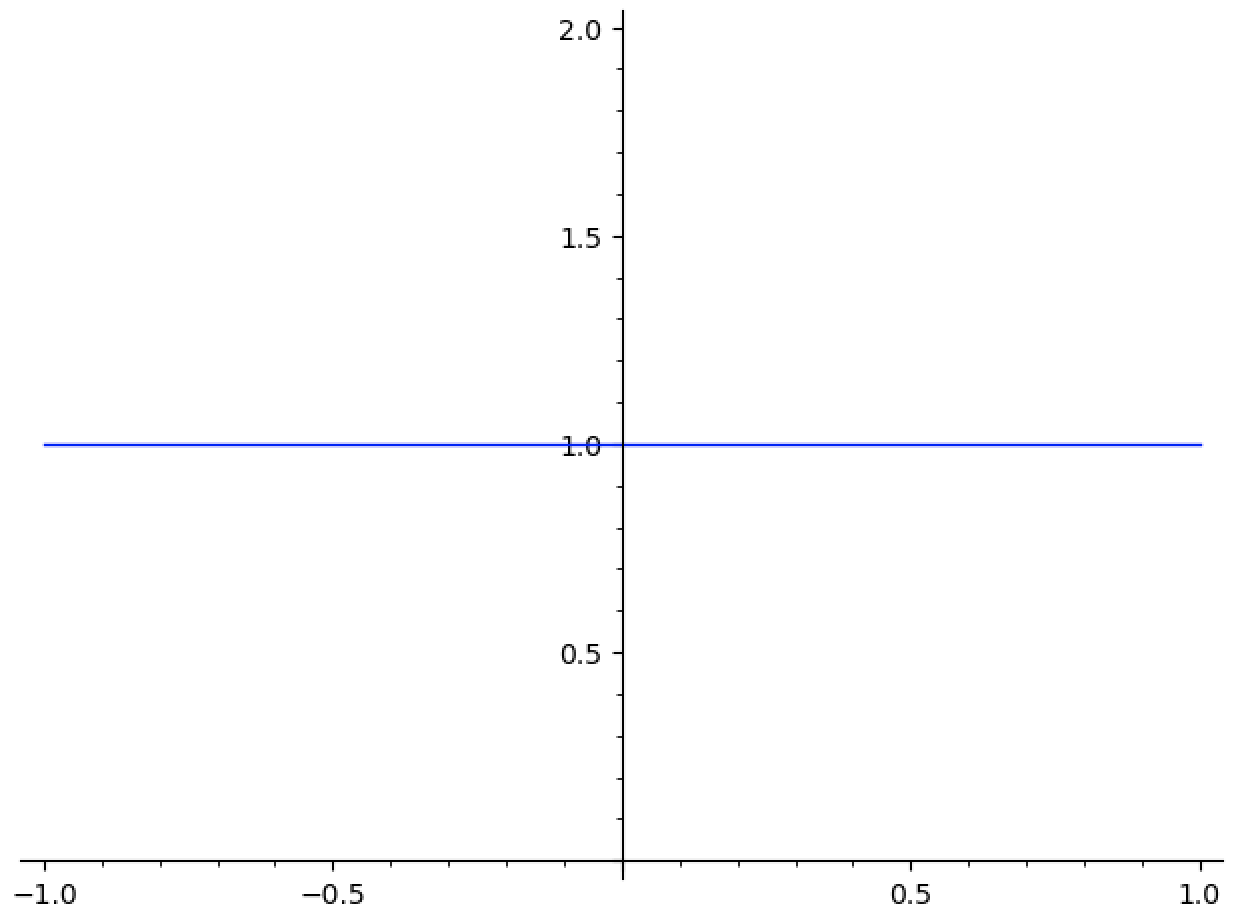
This function doesn’t decay at all, so is certainly not
A less silly example might be
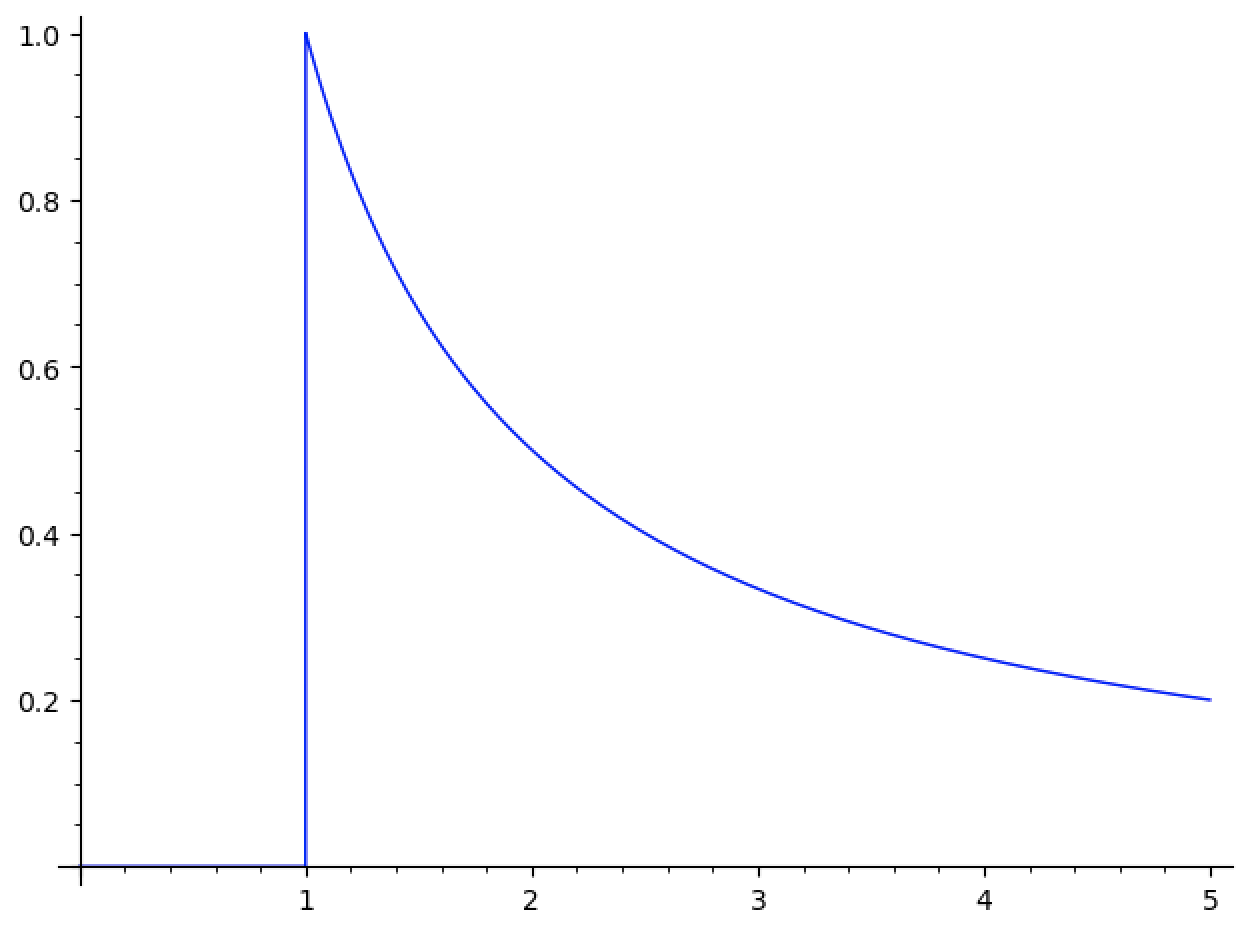
This function decays too slowly to be
The most important cases are
To start, let’s remind ourselves what
As is often the case, we need to treat
Now we can define (for
As usual, we will consider two functions the same if they agree
almost everywhere. We will also often write
It turns out
Let’s see some important examples of
-
If
-
Sometimes
-
Another important example is the circle
-
An example in a different vein is
-
The counterpoint to example (3) is
One of the most important tools we have for proving properties about
These sets of functions are dense in
-
Simple Functions (with finite-measure support). That is, functions of the form
-
Continuous Functions (with compact support). Obviously these are great. We don’t always need the extra power of compact support, but it’s good to know it’s there!
These families of dense functions require a notion of differentiation.
They’re definitely true in
-
Smooth Functions (with compact support). We love differentiation in this household.
-
Schwarz Functions. As long as we’re discussing things that only work in
These families of functions also require some compactness condition (because we’re using the stone-weierstrass theorem).
-
Polynomials. On
-
Polynomials in
There’s actually a kind of master theorem for density results in
Before we move on, these density results are one potential source of
motivation for
This is one reason that
Perhaps the most important inequality associated with
If
This includes the formal case where
This condition on
Here we might think of
From this, one might ask if we actually have equality above. If you’re feeling
particularly optimistic, you might even wonder if we can characterize which
functionals in
Now for the magic part:
For
where
When
The proof of this fact actually goes through complex valued measures!
If
Notice this means that for
so
Frequently one has a function
For instance, when doing fourier analysis, our hilbert space techniques only
work for
With that said, here are the main theorems for useful inclusions:
If
Formally, if
(As an easy exercise, you should prove this)
If
Formally, if
(Again, this is a fairly easy exercise)
In fact, both of the above statements are equivalences.
So going down is allowed if and only if
Notice how these line up with the singularity/rapid decay tradeoff we
mentioned earlier. If
Conversely, if there are sets of minimal measure, then (intuitively) any singularity on one of your atoms can’t be avoided, and we get the inclusion of “rapidly decaying” functions into “slowly decaying” functions with no further qualifications15.
Of course, once we know that, say
It turns out that
We also have interpolation functions which, if
If
That is, every
If
That is, the
In fact, we have the bound
for
Alright, that was another huge information dump! This post felt less like a
motivated tour through
I’ve learned from my mistakes, and I’m not going to try and give a concrete date for the next post. All I’ll say is: See you soon ^_^
-
I’ve been busier than expected… So much for one post a day, haha. ↩
-
The notation comes from a (non-obvious) theorem that
-
This is one pressing reason to quotient by almost-everywhere equivalence. Do you see why
One reasonable question might be whether we can always find a canonical representative for a given equivalence class modulo nullsets. That is, given a “function” in
This is an extremely interesting question, and is the fundamental question in lifting theory. ↩
-
Don’t worry – we’ll be talking a lot about banach spaces in an upcoming post. But
-
We’ll talk about Fourier theory in an upcoming post too! ↩
-
Recall we define the lebesgue integral of
-
This is in line with an apocryphal quote of Grothendieck (which is probably not actually his) that it’s better to have good categories with bad objects, than bad categories with good objects.
That is, we want our categories to have all limits, colimits, exponentials, etc. even if it means introducing “pathological” objects. It’s easier to know you can take limits and worry about what the result looks like later than it is to constantly worry about whether you can take the limit at all.
Similarly, from an analytic lens, it’s better to have a complete space (which admits potentially ugly functions) than it is to have an incomplete space in which every function is nice. ↩
-
You need boundedness in order to guarantee that the sup norm
-
Actually, we can get by with slightly less.
We always have a natural map
It turns out this map is an isometric embedding if and only if
Moreover, this map is surjective (and thus an isometry) when
-
To build a functional on
We’ll talk more about the Hahn-Banach theorem in a future post, but importantly it relies on the axiom of choice! There are actually models of set theory where Hahn-Banach fails, and which think that
-
The question of which
As an aside that I can’t help but mention, apparently there is a banach space which is isomorphic to its double dual, but for which the canonical evaluation map is not the isomorphism! It’s called James’s Space, for the interested. ↩
-
For instance, an integral that takes values in a banach space might not satisfy the radon-nikodym theorem. If your banach space is reflexive, though, then it does. This came from the linked mse question, so I might be misquoting the result or dropping some hypotheses, but this already makes the notion of reflexivity seem more interesting. ↩
-
For proofs of these exercises, and indeed proofs of the stronger equivalences, see here ↩
-
This may require some meditation.
The idea is that we don’t care if a function is singular as long as the infinity can be contained to a set of small enough measure. But if there are no sets of “small enough” measure, then any singularity is bad. ↩
-
In the motivational section before this, we mention that
-
In the sense that meagre sets and nullsets both form
For instance, fat cantor sets can have arbitrarily large measure (in particular, they are not null) yet they are always meagre. ↩